For many years now, I have been trying and (mostly) failing at using some sort of digital camera when testing the optics of the mirrors we fabricate and evaluate at the ATM workshop at the Chevy Chase Community Center here in DC.
I can now report that there finally is some useful and non-vignetted light at the end of the testing tunnel!

I used an old Canon FD film camera lens (FL=28 mm) that I got about 40 years ago and haven’t used in several decades to get a bunch of really nice knife-edge images of a 16″ Meade mirror, located on a stage that can be moved forward and back in whatever steps I like by a smartphone app and a stepper motor setup that Alan Tarica and Pratik Tambe designed and put together.
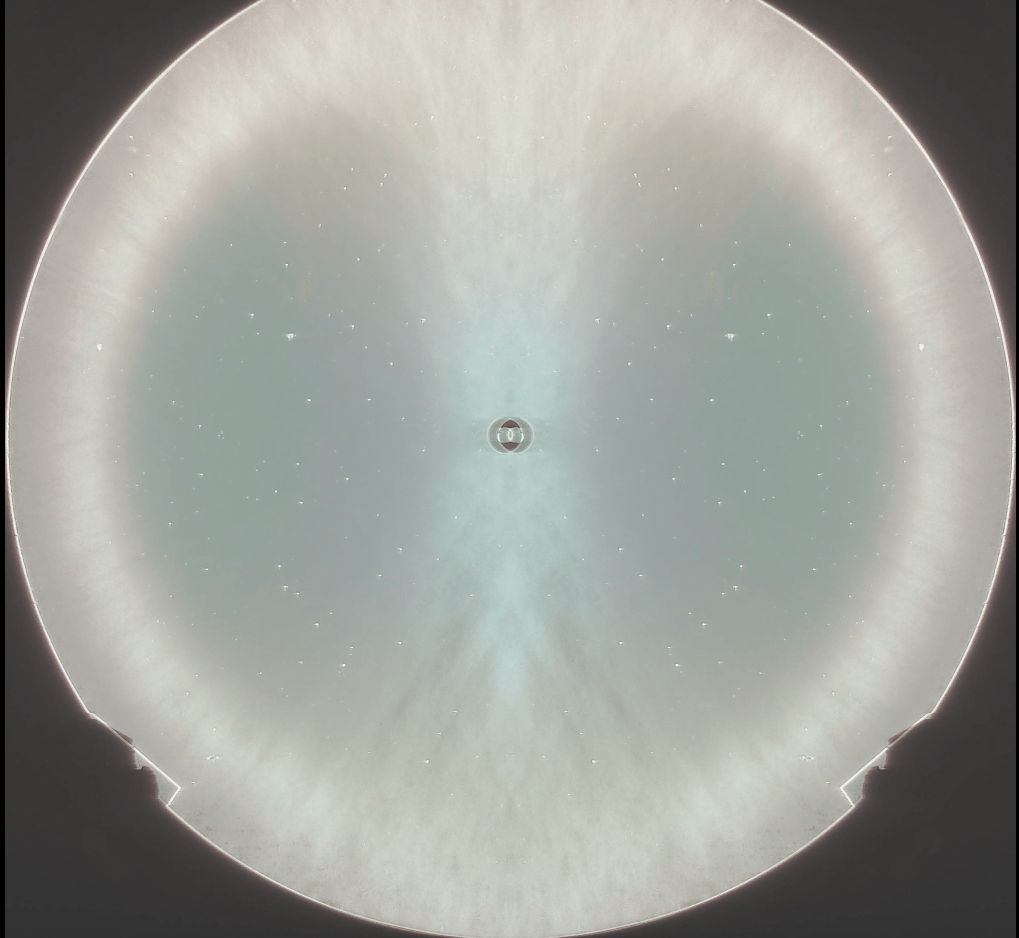
Just now, I finally figured out how to use IrfanView to take one of the images, flip it left-to-right (that is, across the y-axis) and superimpose one onto the other with 50% transparency. A bright ring appeared, which shows the circular ring or zone where the light from our LED, located just under the camera lens, goes out to the mirror and bounces directly back to the lens and is captured by the sensor as a bright ring.
I then captured and pasted that image into Geometer’s Sketchpad, which I used to draw and measure the radii of two circles, centered at the doughnut marking the center of the mirror. This is a somewhat crude measurement of the radii, but it appears that this zone is is at 83% of the diameter (or radius) of the original disk, which is 16 inches across.
Now I just need to do the same thing for all of the other images, and then correlate the radii of the bright zones with the longitudinal (z-axis) motion of the camera and stand, and I will know how close this mirror is to a perfect paraboloid.
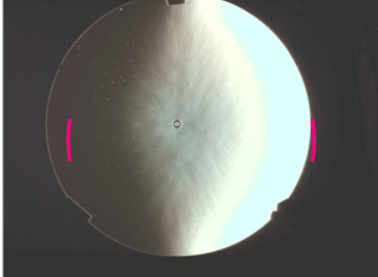
There is an app that supposedly does this for you, called Foucault Unmasked, but it doesn’t seem to work well at all. As you can see from these images, FU is unable to find zones that are symmetrically placed on either side of the center of the mirror. I don’t know what algorithm FU uses, but it sure is f***ed up.
Thanks a lot to Tom Crone, Gert Gottschalk, Pratik Tambe, Alan Tarica, and Alin Tolea for their help and suggestions!


