Tags
astronomy, Astrophotography, ATM, celestron, dobsonian, Optics, science, space, StarSense, Telescope, testing
Astronomy is moving so fast, it’s amazing.
We only truly discovered the nature of galaxies, of nuclear fusion, and of the scale of the universe a mere century ago.
Dark matter was discovered by Vera Rubin just over 40 years ago and dark energy a few years later, just before the time that both professional and amateur astronomers began switching over to CCD and later CMOS sensors instead of film
The first exoplanet was discovered only 30 years ago, and the count is now up to almost six thousand of them (as of 1/21/2024).
While multi-billion dollar space telescopes and giant observatories at places like Mauna Kea and the Atacama produce the big discoveries, amateur astronomers with a not-outrageous budget can now afford to purchase relatively small rigs armed with excellent optics and complete computer control, and lots of patience and hard work, can and so produce amazing images like the ones here https://www.novac.com/wp/observing/member-images/ or this one https://www.instagram.com/gaelsastroportrait?igsh=cjMzYWlqYjNzaDlw, by one of the interns on this project. Gael’s patience, cleverness, dedication and follow-through are all praiseworthy.
However, it is getting harder and harder every year for people to see anything other than the brightest planets, because of ever-increasing light pollution; the vast majority of the people in any of the major population centers on any continent have no hope of seeing the Milky Way from their homes unless there is a wide-spread power outage. Here in the US, such power outages are rare, which means that if you want to go out and find a Messier object, you pretty much cannot star-hop, because you can only see four to ten stars in the entire sky!
One choice is to buy a completely computer-controlled SCT like the ones sold by Celestron. They aren’t cheap, but they will find objects for you.
But what if you don’t want another telescope, but instead want to give nice big Dobsonian telescope the ability to find things easily, using the capabilities inside one’s cell phone?
Some very smart folks have been working on this, and have come up with some interesting solutions. When they work, they are wonderful, but they sometimes fail for reasons not fully understood. I guess it has something to do with the settings in the cell phone being used.
The rest of this will be on one such solution, a commercial one called StarSense from Celestron that holds your phone in a fixed position above a little mirror, and you aim the telescope and your cell phone’s camera at something like the top of a tower far away. Then it uses both the interior sensors on your cell phone and images of the sky to figure out where in the sky your scope is pointing, and tells you which way to push it to get to your desired target.
When it works, it’s great. But it sometimes fails.
You have to buy an entire set from Celestron – one of their telescopes (which has the gizmo built in) along with the license code to unlock the software.
You supply the cell phone.
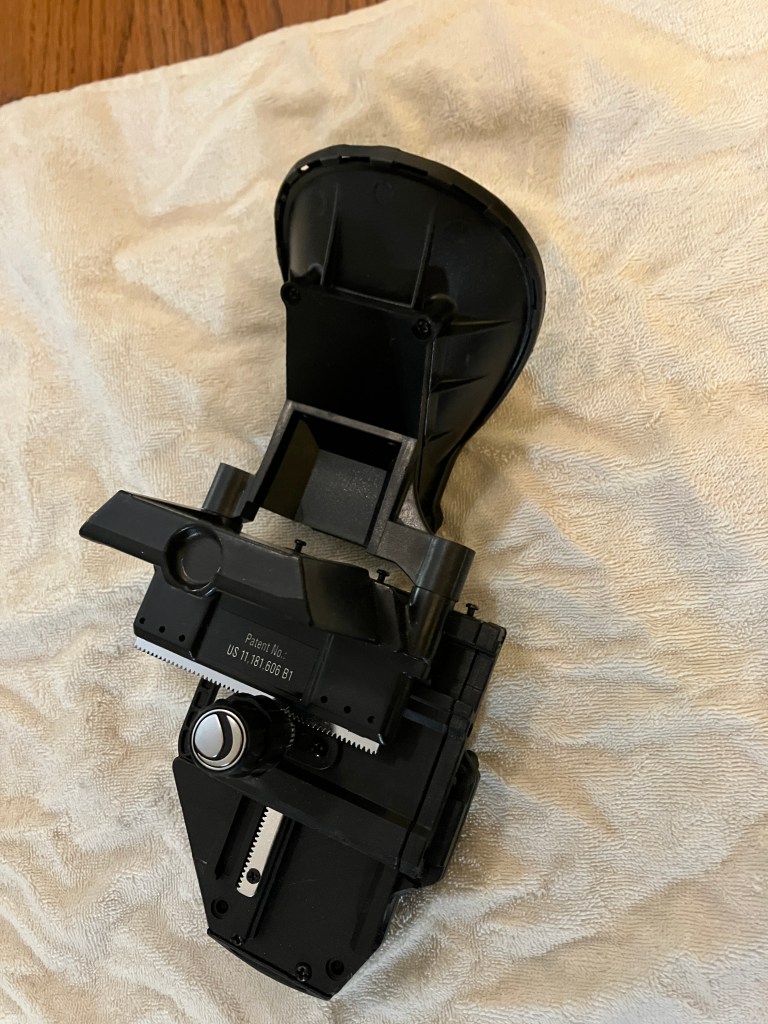
The entire setup ranges in price from about $200 to about $2,000. You cannot just buy the holder and the code from them; you must buy a telescope too. I already had decent telescopes, which I had made, so I bought the lowest-priced one. I then unscrewed the plastic gizmo, and carved and machined connection to a male dovetail slide for it. I also fastened a corresponding female dovetail to each of my scopes. The idea was to then slip this device off or onto whichever one of my telescopes is going to get used that night, as long as I that has a vixen dovetail saddle, and put inexpensive saddles on several scopes I have access to.
Here are some photos of the gizmo:
NCA’s current interns (Nabek Ababiya and Gael Gomez) and I were wondering about the geometry of the angles at which StarSense would aim at the sky in front of the scope. My guess had been that Celestron’s engineers would make the angles of their device so that the center of the optical pencil hitting the lens dead-on at 90 degrees, and hence coning to a focus at the central pixel of the CMOS sensor, would be parallel to the axis of the telescope tube.
We didn’t want to touch the mirror, because it’s quite delicate. But as a former geometry teacher, I couldn’t leave this one alone, so along with Gael and Nabek I made some diagrams and figured out what the angles had to be if the axis of the StarSense app’s image were designed to be precisely parallel to the axis of the telescope.
In my diagram below, L is the location of the Lens, and IJCK is the cell phone lying snug in its holder. The user can slide the cell phone left and right along that line JD as we see it here, or into out of the plane of the page, but it is not possible to change angle D aka <CDE – it’s fixed by the factory molds to be some fixed angle that we measured with various devices to be 19.0 degrees.
Here is a version of the diagrams we made that showed what we predicted all the angles would be so that optical axis OH will be parallel to the tube axis EBD, and that lens angle ILH is a right angle. We predicted that the mirror’s axis would need to be tilted upwards by an angle of 35.5 degrees (anle HBD).
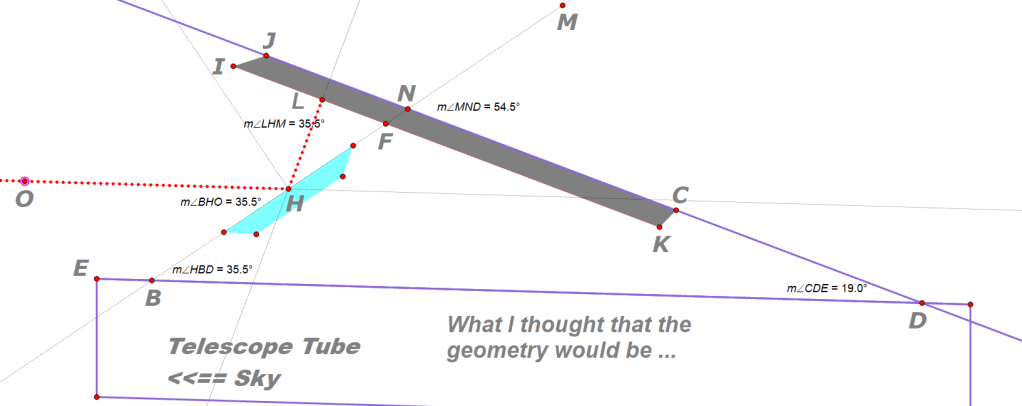
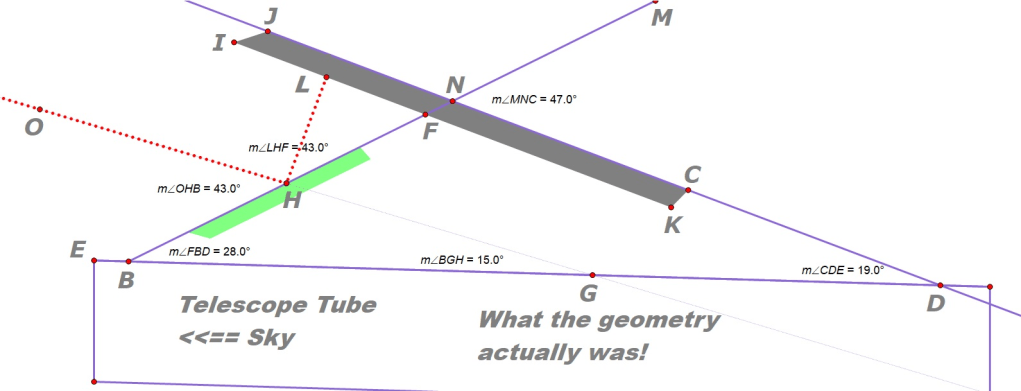
To our surprise, our guesses and calculations were all wrong!
After careful measurements we found that Celestron’s engineers apparently decided that the optical axis of the SS gizmo should instead aim the cell phone’s camera up by 15.0 degrees (angle BGH below). The only parallel lines are the sides of the telescope tube!
We used a variety of devices to measure angle FBD and MNC to an accuracy of about half a degree; all angles turned out to be whole numbers.
Be that as it may, sometimes it works well and sometimes it does not.
Zach Gleiberman and I tested it on an open field in Rock Creek Park here in DC back in the fall of 2024, using the Hechinger-blue 8 inch dob I made 30 years ago and still use. We found that SS worked quite well, pointing us quite accurately to all sorts of targets using my iPhone SE. The sky was about as good as it gets inside the Beltway, and the device worked flawlessly.
Not too long afterwards, I decided to try out an Android-style phone (a REVVL 6 Pro) so that I wouldn’t have to give up my cell phone for the entire evening at Hopewell Observatory. I was unpleasantly surprised to find that it didn’t work well at all: the directions were very far off. I thought it might be because the scope in question had a rather wide plywood ring around the front of its very long tube, and that perhaps too much of the field of view was being cut off?
Why it fails was not originally clear. I thought nearly every modern phone would work, since for Androids, it just needs to be later than 2016 and have a camera, an accelerometer, and gyros, which is a pretty low bar these days. However, my REVVL 6 Pro from T-Mobile is not on the list of phones that have been tested to work!
Part of my assumption that the axis of the SS gizmo would be parallel to the axis of the scope was an explanation that StarSense on had such a large obstruction in front of the SS holder, in the form of a wide wooden disk reinforcing the front of a 10″ f/9 Newtonian, that the SS was missing part of the sky. We now know that’s not correct. It’s an interface problem (ie software) problem.
We think.



